1 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所瞬态光学与光子技术国家重点实验室,陕西 西安 710119
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3 Laboratory of Applied Computational Imaging,Centre Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications,Institut National de la Recherche Scientifique,Université du Québec,Québec J3X1P7,Canada
高速成像技术在物理、化学、生物医学、材料科学及工业等众多领域扮演着十分重要的角色。受电荷存储和读取速度的限制,基于电子成像器件的数码相机成像速度难以进一步提高。近年来,随着成像新技术的发展,超高速和极高速光学成像的性能已得到显著提升,具备更高的时间分辨率、空间分辨率及更大的序列深度等。介绍高速成像技术的发展历程,根据成像方式,将近年来具有代表性的新型超高速和极高速光学成像技术分为直接成像和编码计算成像两个类别。分别介绍和讨论各种新型超高速和极高速光学成像技术的概念和原理,并比较各自的优缺点。最后,对这一领域的发展趋势和前景进行展望。本文旨在帮助研究者系统了解超高速和极高速光学成像技术的基本知识、最新研究发展趋势和潜在应用,为该领域科学研究提供参考。
高速成像 超高速成像 极高速成像 时间分辨率 空间分辨率 序列深度 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(2): 0211020
1 西安建筑科技大学材料科学与工程学院,无机非金属材料国家级实验教学示范中心,西安 710055
2 濮阳濮耐高温材料(集团)股份有限公司,河南 濮阳 457100
活性是轻烧氧化镁的主要应用特性,它与轻烧氧化镁的微观结构密切相关。将新疆某粗晶菱镁矿粉在700~1 100 ℃煅烧制得轻烧氧化镁,对不同温度轻烧氧化镁的晶胞参数、晶粒尺寸、结晶度、比表面积、孔径分布、比孔容、平均孔径、活性和显微结构等进行表征,利用TG结合非等温反应动力学理论研究轻烧氧化镁的微粒结构,分析该微粒结构随温度变化的机理及其对轻烧氧化镁活性的影响。结果表明:从700 ℃至1 100 ℃,轻烧氧化镁晶胞参数a0缩小并趋于稳定,晶粒尺寸逐渐增大,比表面积逐渐减小,但其活性变化并不遵从这一规律,在800 ℃时活性最高;粗晶菱镁矿粉的热分解受相界面上的化学反应所控制,分解产物-轻烧氧化镁“假象”微粒由氧化镁微晶和贯通的气孔网络结构组成;随煅烧温度升高,氧化镁微晶的烧结影响轻烧氧化镁“假象”微粒结构,进而影响其活性;800 ℃轻烧试样晶粒尺寸较小,结晶度较低,比孔容较大,且由于晶格调整使其平均孔径最大,大的孔径有利于溶液进入微粒内部,促进反应进行,因此其活性最高。
粗晶菱镁矿 轻烧氧化镁 活性 macrocrystalline magnesite light-burned magnesia activity
1 西安交通大学第一附属医院眼科,陕西 西安 710061
2 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所瞬态光学与光子技术国家重点实验室,陕西 西安 710119
眼球是机体的视觉器官,同时也是一个良好的光学模型,因此激光技术在眼科得到了广泛的临床应用,覆盖了几乎眼部各个亚专业疾病的诊断与治疗。目前,激光在眼部的应用主要借助其高空间分辨率、高空间定位精度,以及激光的热效应、光化学效应、光爆破效应、光切割效应和生物调节作用等实现。本文综述了激光在眼科各领域的应用现状,并结合激光技术本身的不断发展,总结了激光技术在眼科的临床应用进展及未来可能的突破点。
激光技术 眼科激光应用 光爆破效应 光切割效应 光热效应 光化学效应 光生物调节效应
北京理工大学光电学院光电成像技术与系统教育部重点实验室,北京 100081
重建人体体表三维温度场能够为包括诊断在内的多项人体医学分析提供可靠数据。由于红外成像具有温度测量精度低、成像分辨率不足以及显示效果较差等缺陷,导致重建的目标三维温度场的可靠性存在不足。针对这些问题,提出一种针对人体体表的三维温度场的融合重建方法。即首先采用黑体测温标定的方法,对红外热像仪的测温结果进行误差修正;其次对红外图像进行对比度增强处理;之后进行超分辨率处理,使红外图像在空间分辨率上匹配三维数据;最后在数据融合阶段,基于不同图像中提取到的靶标特征点对应空间中相同位置的事实,对标定得到的系统结构参数进行误差修正。实验表明,该方法使三维温度场的测温精度达到 0.26℃以下,温度场的三维分布结果得到提升,显示效果也得到了增强。
三维温度场重建 热像仪测温标定 多波段光学标定 红外图像处理 人体皮肤特性 3D temperature field reconstruction, temperature c
光子学报
2021, 50(11): 1123001
1 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所瞬态光学与光子技术国家重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710119
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
生物医学研究的发展对光学显微成像的性能,如空间分辨率、成像速度、多维度信息、成像质量等提出了更高的要求。光片荧光显微采用一个薄片光从侧面激发样品,在正交方向探测成像,具有快速三维层析成像和对样品光漂白和光毒性小的优点,是活体生物样品长时间显微观测的理想工具。本文介绍了光片荧光显微成像技术的基本原理及其主要特点;综述了光片荧光显微面临的主要技术问题,以及为解决这些问题而发展出的新原理、新思路和新方法;例举了光片荧光显微成像技术在细胞生物学、发育生物学和神经科学等领域的应用;讨论了该技术的发展趋势及前景。该研究旨在帮助研究者系统了解光片荧光显微成像技术的基本知识、最新研究发展趋势和潜在应用,为该领域科学研究提供参考。
显微 荧光显微 光片照明 三维成像 生物医学成像 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(10): 100001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Department of Bioengineering and the COMSET, Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina 29634, USA
3 State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Science, Xi’an 710119, China
4 Department of Regenerative Medicine and Cell Biology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, South Carolina 29425, USA
5 e-mail: jlqu@szu.edu.cn
6 e-mail: ye7@clemson.edu
Stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy is one of far-field optical microscopy techniques that can provide sub-diffraction spatial resolution. The spatial resolution of the STED microscopy is determined by the specially engineered beam profile of the depletion beam and its power. However, the beam profile of the depletion beam may be distorted due to aberrations of optical systems and inhomogeneity of a specimen’s optical properties, resulting in a compromised spatial resolution. The situation gets deteriorated when thick samples are imaged. In the worst case, the severe distortion of the depletion beam profile may cause complete loss of the super-resolution effect no matter how much depletion power is applied to specimens. Previously several adaptive optics approaches have been explored to compensate aberrations of systems and specimens. However, it is difficult to correct the complicated high-order optical aberrations of specimens. In this report, we demonstrate that the complicated distorted wavefront from a thick phantom sample can be measured by using the coherent optical adaptive technique. The full correction can effectively maintain and improve spatial resolution in imaging thick samples.
Fluorescence microscopy Adaptive imaging Confocal microscopy Scanning microscopy Photonics Research
2017, 5(3): 03000176
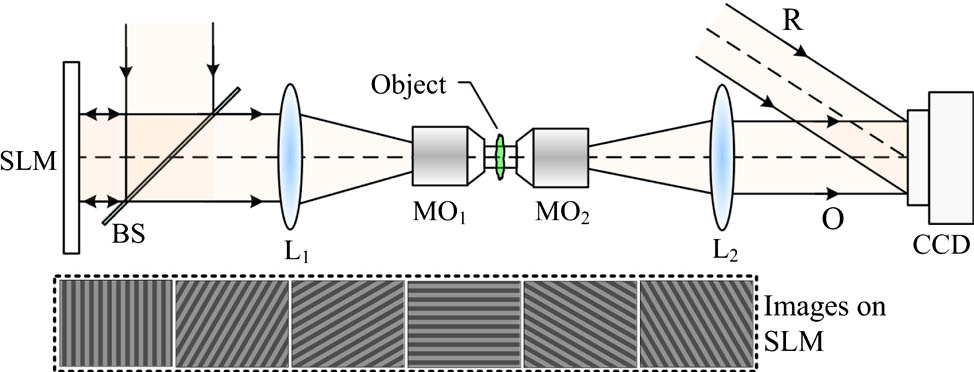
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
2 Institut fur Technische Optik, Universitat Stuttgart, Pfaffenwaldring 9, 70569 Stuttgart, Germany
3 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson-MUSC Bioengineering Program, Charleston, South Carolina 29425, USA
When structured illumination is used in digital holographic microscopy (DHM), each direction of the illumination fringe is required to be shifted at least three times to perform the phase-shifting reconstruction. In this paper, we propose a scheme for spatial resolution enhancement of DHM by using the structured illumination but without phase shifting. The structured illuminations of different directions, which are generated by a spatial light modulator, illuminate the sample sequentially in the object plane. The formed object waves interfere with a reference wave in an off-axis configuration, and a CCD camera records the generated hologram. After the object waves are reconstructed numerically, a synthetic aperture is performed by an iterative algorithm to enhance the spatial resolution. The resolution improvement of the proposed method is proved and demonstrated by both simulation and experiment.
Digital holography Holographic interferometry Interference microscopy Phase measurement Photonics Research
2014, 2(3): 03000087
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Bessel beam propagation in scattering media is simulated using the angular spectrum method combined with slice-by-slice propagation model. Generating Bessel beams with a spatial light modulator, which provides a means to adjust flexibly the parameters of the Bessel beam, allows us to validate the simulation results experimentally. The study reveals that the self-reconstructing length changes oppositely with the axicon angle (i.e., the larger the axicon angle, the shorter the self-reconstructing length). The radius of the incident beam has little influence on the self-reconstruction of the Bessel beam central lobe.
260.1960 Diffraction theory 170.3660 Light propagation in tissues 290.7050 Turbid media Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(11): 112601
1 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所瞬态光学与光子技术国家重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710119
2 中国科学院研究生院, 北京 100049
3 西安理工大学应用物理系, 陕西 西安 710048
腔倒空技术是一种有效产生大能量、短脉冲激光输出的调Q技术,其产生的Q开关激光脉冲的宽度主要由谐振腔腔长决定。大孔径半绝缘GaAs光电导开关(PCSS)是一种可耐高压的光控开关,具有响应速度快、时间抖动小、耐压高、暗电阻大、导通电阻小等特点,将其直接作为控制腔倒空激光器的光反馈回路和高电压开关,在腔长为20 cm的氙灯抽运Nd:YAG电光调Q激光器上实现了激光波长1064 nm、单脉冲能量15 mJ、脉冲半峰全宽 (FWHM)为1.7 ns的腔倒空激光脉冲稳定输出,脉冲宽度峰峰值抖动优于7%,能量峰峰值抖动优于3%。
激光技术 电光调Q 腔倒空 稳定腔 GaAs光电导开关 Nd:YAG激光器





